空のUPDATEによるDEADLOCK
概要
負荷検証中に deadlock のログを見つけて、その対処をしたのでメモです。
クエリ特定
SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS; コマンドを実行すると、
LATEST DETECTED DEADLOCK でどのクエリで deadlock が発生したのかわかります。
今回は
INSERT INTO tokens (id, token) VALUES(1, 'token'); INSERT INTO tokens (id, token) VALUES(2, 'token2');
のようなクエリで deadlock になっていることがわかりました。
原因&対処
INSERT の直前で、UPDATE tokens SET delete_time=NOW() WHERE id=1; のような UPDATE をしており、
これが空の場合、ネクストキーロックがかかってしまうためとわかりました。
参考
試す。 ターミナル1
mysql> BEGIN; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> UPDATE tokens SET delete_time=NOW() WHERE id=1; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) Rows matched: 0 Changed: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> INSERT INTO tokens (id, token) VALUES(1, 'token'); Query OK, 1 row affected (7.07 sec)
ターミナル2
mysql> BEGIN; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> UPDATE tokens SET delete_time=NOW() WHERE id=2; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) Rows matched: 0 Changed: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> INSERT INTO tokens (id, token) VALUES(2, 'token2'); ERROR 1213 (40001): Deadlock found when trying to get lock; try restarting transaction
Deadlock!!!
対処。
アプリケーションのロジックで、まず、SELECT で存在をチェックして、存在すれば UPDATE する形にしました。
// ロックを避けるために存在チェック
isExist, err := // SELECT * FROM tokens WHERE id=?;
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if isExist {
// UPDATE
}
// INSERT
XXXロックとかの理解を深めないと。。。
あとで読もう
Golang で iOS/Android アプリ内課金の実装
概要
アプリ内課金の実装に関わったので、メモ。
※アプリ内課金はプラットフォーム側の影響を受ける。記載内容が古くなっている可能性があるので注意。
テーブル設計
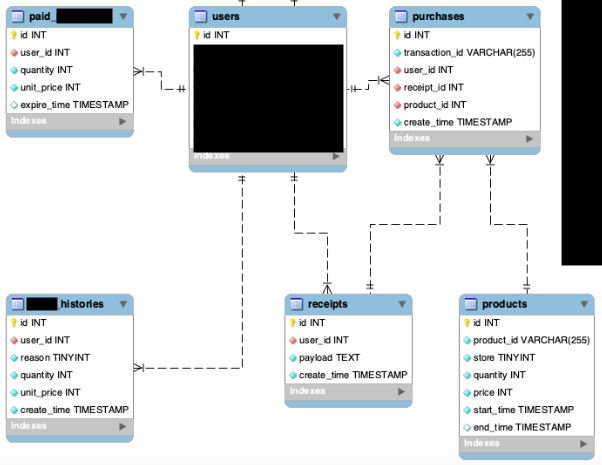
products テーブル
- App Store, Google Play に登録するアプリ内課金アイテムの情報。product_id には "com.example.100gold" などの文字列が入る。
receipts テーブル
- クライアントから送られたレシートをそのまま保存する
purchases テーブル
- tranasction_id カラムは App Store なら Transaction ID を入れ、Google Play なら Order ID を入れる。
paid_golds テーブル
- 有償ゴールドの数
gold_histories テーブル
- 有償ゴールドの購入、使用の履歴
レシートの検証
こちらを使わせていただいた。
AWA で使用されているとのことで、信頼できるし、ありがたい...
自動購読課金について【iOS編】、自動購読課金について【Android編】で課金処理の流れも非常に参考になった。ありがたい...
実装したコード抜粋
// クライアントから送られたレシートの検証後のデータを扱うモデル
package model
type PurchaseOrder struct {
Payload string
Store StoreType // AppStore, GooglePlay
OrderLines []*OrderLine
}
type OrderLine struct {
TransactionID string
OriginalTransactionID string
Quantity int
ProductID string
}
AppStoreValidator
package validator
import (
"context"
"github.com/awa/go-iap/appstore"
)
type AppStoreValidator struct {
Client *appstore.Client
}
// NewAppStoreValidator generates a validator.
func NewAppStoreValidator() *AppStoreValidator {
return &AppStoreValidator{
Client: appstore.New(),
}
}
// Verify sends receipts and gets order lines.
func (v *AppStoreValidator) Verify(ctx context.Context, payload string) ([]*model.OrderLine, error) {
req := appstore.IAPRequest{
ReceiptData: payload,
}
resp := &appstore.IAPResponse{}
err := v.Client.Verify(ctx, req, resp)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if err := handleError(resp.Status); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
var orderLines []*model.OrderLine
for _, iap := range resp.Receipt.InApp {
// 略
orderLines = append(orderLines, order)
}
return orderLines, nil
}
// 成功したら 20x 系、レシートの不備・不正等は 40x 系、サーバエラー時 (クライアントにレシート送信をリトライしてほしい) は 50x 系としたかったので、独自で定義
func handleError(status int) error {
err := appstore.HandleError(status)
if err == nil {
return nil
}
switch status {
case 21000, 21002, 21003, 21004, 21010:
// レシートが不正
return domain.ErrInvalidReceipt
case 21005, 21009:
// サーバ側のエラーなので再送信を促す
// 21009 はたいていの場合は App Store 側の問題であり、リトライを促す旨指示がある
// https://developer.apple.com/library/content/technotes/tn2413/_index.html#//apple_ref/doc/uid/DTS40016228-CH1-RECEIPT-_WHEN_VALIDATING_MY_RECEIPT__THE_APP_STORE_RETURNS_A_STATUS_CODE_OF_21009__
return domain.ErrReceiptValidationFailed
}
if status >= 21100 && status <= 21199 {
return domain.ErrReceiptValidationFailed
}
return err
}
GooglePlayValidator
package validator
import (
"context"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/json"
"github.com/awa/go-iap/playstore"
)
type GooglePlayValidator struct {
Key string
VerifySignature func(base64EncodedPublicKey string, receipt []byte, signature string) (bool, error)
}
type IABPayload struct {
Json string `json:"json"`
Signature string `json:"signature"`
}
type IABReceipt struct {
OrderID string `json:"orderId"`
PackageName string `json:"packageName"`
ProductID string `json:"productId"`
PurchaseTime int64 `json:"purchaseTime"`
PurchaseState int `json:"purchaseState"`
DeveloperPayload string `json:"developerPayload"`
PurchaseToken string `json:"purchaseToken"`
AutoRenewing bool `json:"autoRenewing"`
}
// NewGooglePlayValidator generates a validator.
func NewGooglePlayValidator(key string) *GooglePlayValidator {
return &GooglePlayValidator{
Key: key,
VerifySignature: func(key string, purchaseData []byte, signature string) (bool, error) {
return playstore.VerifySignature(key, purchaseData, signature)
},
}
}
// Verify verifies in app billing signature and gets order lines.
func (v *GooglePlayValidator) Verify(ctx context.Context, payload string) ([]*model.OrderLine, error) {
var iabPayload IABPayload
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(payload), &iabPayload); err != nil {
return nil, domain.ErrInvalidReceipt
}
purchaseData := []byte(iabPayload.Json)
signature := iabPayload.Signature
isValid, err := v.VerifySignature(v.Key, purchaseData, signature)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if isValid == false {
return nil, domain.ErrInvalidReceipt
}
var receipt IABReceipt
if err = json.Unmarshal(purchaseData, &receipt); err != nil {
return nil, domain.ErrInvalidReceipt
}
// もし purchaseState が 0 以外(0: purchased, 1: canceled, 2: refunded) の場合はクライアント起因のエラーとする
if receipt.PurchaseState != 0 {
return nil, domain.ErrInvalidReceipt
}
// クライアント側で DeveloperPayload に ユーザID を入れてもらう
if receipt.DeveloperPayload == userId {
return nil, domain.ErrInvalidReceipt
}
var orderLines []*model.OrderLine
// 略
orderLines = append(orderLines, order)
return orderLines, nil
}
GolangでGooglePlayの課金レシートの署名検証を参考。
レシート検証〜保存
クライアントから store(AppStore / GooglePlay)と payload(購入レシート)を送ってもらう。
こんな感じに。
// レシートの検証を行い、検証後のデータを取得
validator // AppStoreValidator or GooglePlayValidator
orderLines, err := validator.Verify(ctx, payload)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// トランザクション
// ユーザ毎に排他処理を行う
// select users for update
// クライアントから与えられたレシートを保存
// create receipts
for _, orderLine := range orderLines {
// すでに purchases テーブルに TransactionID or OriginalTransactionID が存在していないかチェック
// isExist
// purchase 保存
// create purchases
// 有償ゴールド保存
// create paid_golds
// 履歴保存
// create gold_histories
}
Github Actions で Firebase ファンクションをデプロイする際の注意点
概要
PR をマージしたときに、
Github Actions で Firebase ファンクションをデプロイするようにしたとき、
Github Actions が2回走り、その内1回のデプロイでエラーになりました。
それを解決した時のメモです。
エラー
ログの一部抜粋です。
※Firebase ファンクションに2つ関数があり、Firebase Hosting にもデプロイしています。
1つは成功し、1つはこけている。

ファンクションのデプロイ成功。

ファンクションのデプロイ失敗。

.github/main.workflow (雰囲気です)
workflow "Deploy workflow" {
on = "push"
resolves = ["Deploy"]
}
action "BranchCheck" {
uses = "actions/bin/filter@master"
args = "branch develop"
}
action "Deploy" {
uses = "actions/npm@master"
runs = "sh -c"
args = ["npx firebase deploy --project xxx"]
secrets = ["FIREBASE_TOKEN"]
needs = ["BranchCheck"]
}
原因
ブランチ削除のとき、Github Actions の環境変数 の GITHUB_REF には、デフォルトのブランチ(このリポジトリの場合は develop)が指定される。
よって、PRをマージする際、ブランチを削除するにチェックしていた場合、 develop ブランチかどうかのチェックに通り、デプロイが2回実行されてしまい、その内1回がこけていた。
修正
ブランチ削除の場合のフィルタを入れる。
https://github.com/actions/bin/pull/51 でマージされているのだが、真偽が逆になっているので、やめた。
修正後(雰囲気)
workflow "Deploy workflow" {
on = "push"
resolves = ["Deploy"]
}
action "BranchCheck" {
uses = "actions/bin/filter@master"
args = "branch develop"
}
action "Filter deleted branches" {
uses = "UltCombo/action-filter-deleted-branches@master"
needs = ["BranchCheck"]
}
action "Deploy" {
uses = "actions/npm@master"
runs = "sh -c"
args = ["npx firebase deploy --project xxx"]
secrets = ["FIREBASE_TOKEN"]
needs = ["Filter deleted branches"]
}
Docker コマンドメモ
概要
Dockerコマンド、毎回ググってる気がするので、自分用のメモ。
コマンド
ビルド
docker build -t [イメージ名] .
ARG を使う場合、DockerfileにARGを定義して
docker build --build-arg TOKEN=$TOKEN -t [イメージ名] .
タグ
docker tag [イメージID] [イメージ名]:[タグ名]
DockerHubにあげる
docker push [イメージ名]:[タグ名]
コンテナを起動して、中に入る
docker run -it [イメージ名]:[タグ名] /bin/sh
環境変数あり
docker run -it -e TOKEN=$TOKEN [イメージ名]:[タグ名] /bin/sh
Github Actions で Go のテストを実行する。その2
概要
こちらに加え、go get でプライベートリポジトリのライブラリを使いたくなった。
手順
コード
.github/main.workflow
workflow "Test workflow" {
on = "push"
resolves = "Test Action"
}
action "Test Action" {
uses = "docker://golang:1.11"
secrets = ["ACCESS_TOKEN"]
runs = "sh -c"
args = ["./.github/script.sh"]
}
.github/script.sh
#!/bin/sh
set -e
git config --global url."https://${ACCESS_TOKEN}:x-oauth-basic@github.com/".insteadOf "https://github.com/"
go test -v ./...
DeleGateのコンテナイメージを公開した
SOCKS プロキシサーバーの DeleGate をコンテナで立てたかったのだが、
docker hub で上位にあったイメージがエラーで使えなかった。 hub.docker.com
$ docker-compose up
Creating delegated_delegated_1 ... done
Attaching to delegated_delegated_1
delegated_1 | #### in default conf: DGROOT='/tmp'
delegated_1 | #### loading default conf: /bin/../etc/delegated.conf
delegated_1 | #### loading conf: -> file:/bin/../etc/delegated.conf
delegated_1 | (UNIX) 02:00:33.780 [ 1] ##fopen_PATHX(r) ign.dir.{/usr/lib}/usr/lib/ssl <= dl.c:274
delegated_1 | -- ERROR: can't link the SSL/Crypto library.
delegated_1 | -- Hint: use -vl option to trace the required library,
delegated_1 | --- find it (ex. libssl.so.X.Y.Z) under /usr/lib or /lib,
delegated_1 | --- then set the library version as DYLIB='+,lib*.so.X.Y.Z'
どうやら OpenSSL のバージョンと合ってないよう...
AWSのコンテナ関連サービスを調べる
概要
AWSのコンテナ関連サービスを調べた。
AWSのコンテナ関連サービス

ECS/EKS/Fargate/EC2
コントロールプレーン
コンテナの管理:クラスターで Docker コンテナを簡単に実行、停止、管理できる
ECS
Cluster > Service > Task difinition > Container definition という概念がある。
Kubernetes の Cluster(Node) > Ingress(Service) > Deployment > Pod とよく似た概念と思われる。
EKS
Kubernetes を使用する場合はこれ。
標準的な Kubernetes 環境で実行されるアプリケーションは EKS と完全な互換性がある。
データプレーン
EC2(Fargate) を使用して ECSを使う、EC2を使用して EKS を使うという形になる。
Fargate
サーバーやクラスターの管理の必要なしにコンテナを実行できる。
-> コンテナを実行するために仮想マシンのクラスターをプロビジョニング、設定、スケールする必要がない。
-> 従来のEC2の場合は、「これ以上コンテナを増やしたらメモリが不足しそうだから、EC2のインスタンスタイプを変えようかな」がある。
2019年2月現時点ではEKSには対応していない。
EC2
高スペックのEC2を事前に選んでおけば、Fargate より速度が向上できることもある。
Elastic Beanstalk
Elastic Beanstalk Multi-container Docker
Elastic Beanstalk は Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) を使用して、マルチコンテナ Docker 環境へのコンテナのデプロイを調整します。Amazon ECS には、Docker コンテナを実行するインスタンスのクラスターを管理するためのツールが用意されています。Elastic Beanstalk は、クラスターの作成やタスクの定義と実行などの Amazon ECS タスクを処理します。
Elastic Beanstalk でも ECS を使っている
EC2でDocker
EC2 インスタンスに Docker をインストールして、Docker コンテナを実行することも可能。
GCE で Docker コンテナを実行できるのと同様。
所感
AWS でコンテナを実行する(k8sでない)なら ECS + Fargate が良さそう。
インフラを意識せず済み、冗長化・スケールなども問題なさそう。
で、Beanstalk Multi-container Docker がどうなのか...
ECS+Fargate vs ElasticBeanstalk
ネットより
http://labs.septeni.co.jp/entry/2016/04/05/105249
何がどう違うの?というところが解らなかったので、AWSのソリューションアーキテクトの方に弊社へ来ていただいてサービスのご紹介を頂きました。 Beanstalkの中でECSが動いているので大きな違いはありませんが、Beanstalkの方は元々PaaSなので、色々元々組み込まれて便利に使え、.ebextensionsというYAMLで管理できるようになっていいます。 ECSはdockerに特化したもので、最新機能はECSの方が組み込まれるのが早いそうです。 .ebextensionsを使っていくと何でもできちゃうので運用めっちゃ大変そうだなーと思って、シンプルにECSを試しました。
https://qiita.com/naomichi-y/items/d933867127f27524686a
Beanstalk Multi-container Dockerは、ECSを抽象化してRDSやログ管理の機能を合わせて提供してくれる。ボタンを何度か押すだけでRubyやNode.jsのアプリケーションが起動してしまう。 一見楽に見えるが、ブラックボックスな部分もありトラブルシュートでハマりやすいので、素直にECSを使った方が良いと思う
https://www.wantedly.com/companies/pring/post_articles/124469

両方試した
両方試してみて、最初、
- ElasticBeanstalk の方が環境構築、デプロイが楽。
- ElasticBeanstalk のコンソール画面で一括で確認できるのも良さそう。
と思ったが、、、
ecs-deployを使ってみたところ、ElasticBeanstalk のデプロイ面での優位はなくなった...
環境構築の手間もそんなに変わらないし、
ElasticBeanstalk のコンソール画面で一括で確認できる点、コード量が若干少ない点もどうだろう...
ECS Fargate を使うのが良さそうと思った。